Radon gas is a cancer-causing gas that is naturally occurring and is invisible, odorless, and permeates through the soil. Any type of home is at risk for high levels of radon gas including homes with slab or crawlspace foundations, and can be found in schools and commercial property as well. Basement homes can have high levels as the soil excavation process can open up "pockets" of radon gas. The radon gas levels can even vary between adjoining homes and generally speaking, any structure should be tested. Radon gas can enter structures through cracks in solid floors and walls, construction joints, gaps around service pipes, cavities in walls and through the water supply, and is the highest cause of lung cancer amongst non-smokers.
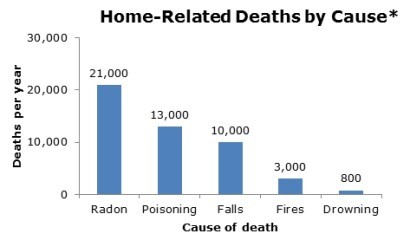
Radon is estimated to cause about 21,000 lung cancer deaths per year.
The numbers of deaths from other causes are taken from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's 1999-2001 National Center for Injury Prevention and Control Report and 2002 National Safety Council Reports. Lifetime risk of lung cancer deaths from EPA Assessment of Risks from Radon in Homes (EPA 402-R-03-003). Data listed is from the US EPA (EPA.gov/radon)
High levels of radon gas can be remedied through a mitigation system and can reduce the levels by up to 99%. On a national average, 1 in 15 homes have high levels of radon gas and the only way to protect your home is through testing.
See www.epa.gov/radon/ for more information.
